BAR Implements Updated Diesel Smog Check Standards
On July 5, 2023, the Bureau of Automotive Repair (BAR) implemented updated Smog Check On-Board Diagnostic II (OBD) readiness standards for 2007 and newer light-duty diesel vehicles. The prior standards permitted up to two readiness monitors to be unset to pass a Smog Check inspection. The new standards now allow only the Diesel Particulate Filter and the Non-Methane Hydrocarbon Catalyst readiness monitors to remain unset.
The new standards were established by examining the impact of the proposed readiness standards on vehicles that had undergone a minimum of 15 restarts and added 200 miles on the vehicle odometer since the last reset of the readiness monitors. The analysis demonstrated that most vehicles could reasonably meet the proposed standards. Vehicles with design-related issues that prevent them from meeting the new standards have been identified and are exempt from meeting the new standards until the vehicle manufacturer corrects the design issues. These vehicles are identified on the On-Board Diagnostic Test Reference webpage.
As anticipated, failure rates after implementation of the new standards fell below the projected rates had the new standards not been implemented. This outcome can be attributed, in part, to Smog Check repair technicians working with vehicle owners to adequately prepare their vehicles for inspection. The new standards also resulted in greater detection of vehicles with OBD II malfunctions that were subsequently repaired in order to pass the Smog Check inspection. Additional analysis also revealed that some vehicles with illegally modified software that had previously passed Smog Check inspections did not pass the new standards and, thus, required the vehicle owners to install approved software. Overall, the implementation of new readiness standards has proven successful and will enhance the effectiveness of California’s Smog Check Program.
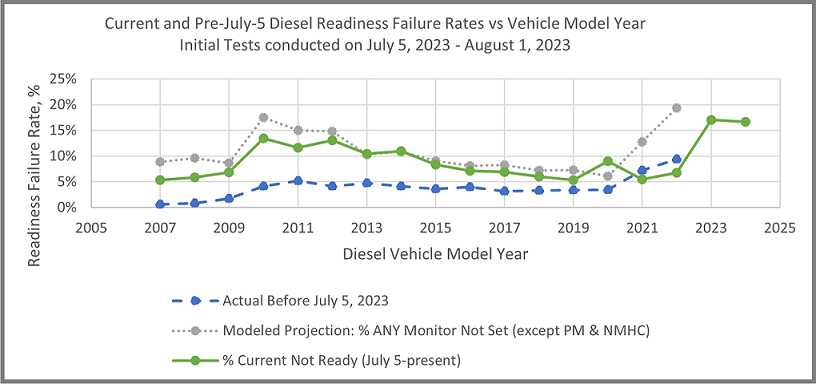
The chart details Smog Check readiness failure rates before and after implementation of the new readiness standards. The dashed blue line indicates the readiness failure rates prior to implementation of the new standards. The dotted grey line shows the projected failure rate for the new standards. The solid green line shows the actual readiness failure rate after implementation.
